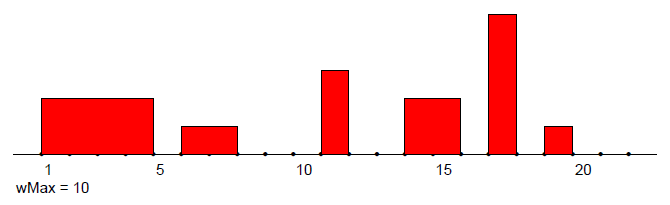
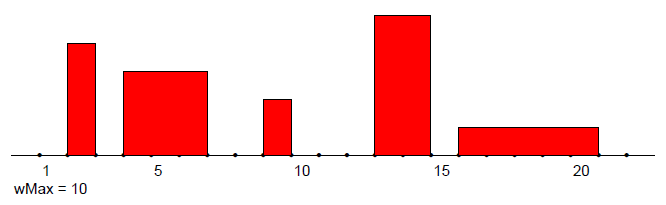
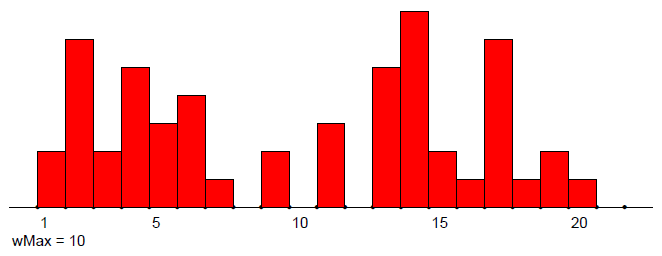
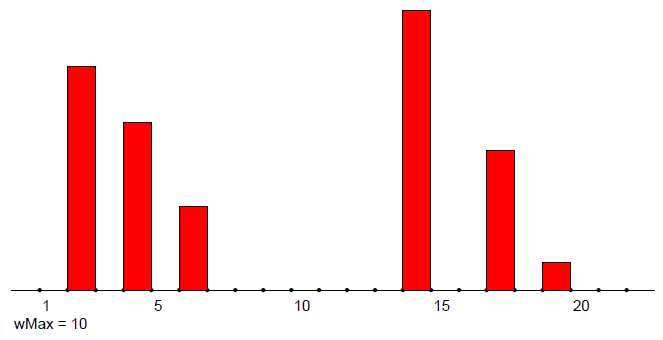
Temporal networks (with 0 transition time)
John S. Baras, George Theodorakopoulos: Path Problems in Networks. (2010)
Slides from Sredin seminar 1220
Notes from Sredin seminar 1226 (in Slovene)
timer.zip ZIP with data and programs
Infinity in Python
>>> inf = float("inf")
>>> inf
inf
>>> inf+3
inf
>>> inf*inf
inf
⌘
In the following I present an implementation (March 10, 2014) of operations on temporal quantities restricted to the case of intervals of type 2 = [). In the examples I will only use the integer time values.
Addition and multiplication of temporal quantities
inf = float("inf")
a = [(1,5,2), (6,8,1), (11,12,3), (14,16,2), (17,18,5), (19,20,1)]
b = [(2,3,4), (4,7,3), (9,10,2), (13,15,5), (16,21,1)]
N = []
E = [(1,inf,1)]
def get(S):
try: return(next(S))
except StopIteration: return((inf,inf,0))
def plus(a,b): return(a+b)
def times(a,b): return(a*b)
def standard(a):
if len(a) == 0: return(a)
fc = inf; c = []
for (sa,fa,va) in a:
if fc == sa:
if vc == va: fc = fa
else:
c.append((sc,fc,vc))
vc = va; sc = sa; fc = fa
else:
if fc != inf: c.append((sc,fc,vc))
sc = sa; fc = fa; vc = va
c.append((sc,fc,vc))
return(c)
def sum(a,b):
if len(a) == 0: return(b)
if len(b) == 0: return(a)
c = []; A = a.__iter__(); B = b.__iter__()
(sa,fa,va) = get(A); (sb,fb,vb) = get(B)
while (sa<inf) or (sb<inf):
if sa < sb:
sc = sa; vc = va
if sb < fa: fc = sb; sa = sb
else: fc = fa; (sa,fa,va) = get(A)
c.append((sc,fc,vc))
elif sa == sb:
sc = sa; fc = min(fa,fb); vc = plus(va,vb)
c.append((sc,fc,vc))
sa = sb = fc; fA = fa
if fA <= fb: (sa,fa,va) = get(A)
if fb <= fA: (sb,fb,vb) = get(B)
else:
sc = sb; vc = vb
if sa < fb: fc = sa; sb = sa
else: fc = fb; (sb,fb,vb) = get(B)
c.append((sc,fc,vc))
return(standard(c))
def prod(a,b):
if len(a)*len(b) == 0: return([])
c = []; A = a.__iter__(); B = b.__iter__()
(sa,fa,va) = get(A); (sb,fb,vb) = get(B)
while (sa<inf) or (sb<inf):
if fa <= sb: (sa,fa,va) = get(A)
elif fb <= sa: (sb,fb,vb) = get(B)
else:
sc = max(sa,sb); fc = min(fa,fb); vc = times(va,vb)
c.append((sc,fc,vc))
if fc == fa: (sa,fa,va) = get(A)
if fc == fb: (sb,fb,vb) = get(B)
return(standard(c))
print("a =",a); print("b =",b)
d = sum(a,b); print("d =",d)
e = prod(a,b); print("e =",e)
Results
plus = + ; times = *
>>>
a = [(1, 5, 2), (6, 8, 1), (11, 12, 3), (14, 16, 2), (17, 18, 5), (19, 20, 1)]
b = [(2, 3, 4), (4, 7, 3), (9, 10, 2), (13, 15, 5), (16, 21, 1)]
s = [(1, 2, 2), (2, 3, 6), (3, 4, 2), (4, 5, 5), (5, 6, 3), (6, 7, 4), (7, 8, 1), (9, 10, 2),
(11, 12, 3), (13, 14, 5), (14, 15, 7), (15, 16, 2), (16, 17, 1), (17, 18, 6), (18, 19, 1),
(19, 20, 2), (20, 21, 1)]
p = [(2, 3, 8), (4, 5, 6), (6, 7, 3), (14, 15, 10), (17, 18, 5), (19, 20, 1)]
>>> sum(a,N)
[(1, 5, 2), (6, 8, 1), (11, 12, 3), (14, 16, 2), (17, 18, 5), (19, 20, 1)]
>>> sum(N,N)
[]
>>> prod(a,N)
[]
>>> prod(N,N)
[]
>>> prod(a,E)
[(1, 5, 2), (6, 8, 1), (11, 12, 3), (14, 16, 2), (17, 18, 5), (19, 20, 1)]
>>> prod(E,E)
[(1, inf, 1)]
>>> print("a =",a); print("b =",b)
a = [(1, 5, 2), (6, 8, 1), (11, 12, 3), (14, 16, 2), (17, 18, 5), (19, 20, 1)]
b = [(2, 3, 4), (4, 7, 3), (9, 10, 2), (13, 15, 5), (16, 21, 1)]
>>> d = sum(a,b); print("d =",d)
d = [(1, 2, 2), (2, 3, 6), (3, 4, 2), (4, 5, 5), (5, 6, 3), (6, 7, 4), (7, 8, 1),
(9, 10, 2), (11, 12, 3), (13, 14, 5), (14, 15, 7), (15, 16, 2), (16, 17, 1),
(17, 18, 6), (18, 19, 1), (19, 20, 2), (20, 21, 1)]
>>> e = prod(a,b); print("e =",e)
e = [(2, 3, 8), (4, 5, 6), (6, 7, 3), (14, 15, 10), (17, 18, 5), (19, 20, 1)]
a:
b:
a+b:
a*b:
Connectivity semiring ({0,1},∨,∧,0,1).
def binary(a):
c = []
for (sa,fa,va) in a:
if va > 0: c.append((sa,fa,1))
return(c)
ba = binary(a); bb = binary(b)
def plus(a,b): return(max(a,b)) # OR
def times(a,b): return(min(a,b)) # AND
print("ba =",ba); print("bb =",bb)
d = sum(ba,bb); print("d =",d)
e = prod(ba,bb); print("e =",e)
print("E+ba =",sum(E,ba))
print("E+E =",sum(E,E))
we get
ba = [(1, 5, 1), (6, 8, 1), (11, 12, 1), (14, 16, 1), (17, 18, 1), (19, 20, 1)] bb = [(2, 3, 1), (4, 7, 1), (9, 10, 1), (13, 15, 1), (16, 21, 1)] d = [(1, 8, 1), (9, 10, 1), (11, 12, 1), (13, 21, 1)] e = [(2, 3, 1), (4, 5, 1), (6, 7, 1), (14, 15, 1), (17, 18, 1), (19, 20, 1)] E+ba = [(1, inf, 1)] E+E = [(1, inf, 1)]
Shortest path semiring (ℝ+0,min,+,∞,0).
plus = min ; times = +
>>>
def plus(a,b): return(min(a,b))
def times(a,b): return(a+b)
E = [(1,inf,0)]
print("a =",a); print("b =",b)
d = sum(a,b); print("d =",d)
e = prod(a,b); print("e =",e)
print("E+a =",sum(E,a))
print("E+E =",sum(E,E))
>>>
a = [(1, 5, 2), (6, 8, 1), (11, 12, 3), (14, 16, 2), (17, 18, 5), (19, 20, 1)]
b = [(2, 3, 4), (4, 7, 3), (9, 10, 2), (13, 15, 5), (16, 21, 1)]
d = [(1, 5, 2), (5, 6, 3), (6, 8, 1), (9, 10, 2), (11, 12, 3), (13, 14, 5), (14, 16, 2), (16, 21, 1)]
e = [(2, 3, 6), (4, 5, 5), (6, 7, 4), (14, 15, 7), (17, 18, 6), (19, 20, 2)]
E+a = [(1, inf, 0)]
E+E = [(1, inf, 0)]
In this semiring the absorption law holds: E + a = E .
Closure
Let (A,+,.,0,1) be a semiring. Then also the structure (A(T),⊕,⊙,N,E) of temporal quantities over (A,+,.,0,1) is a semiring; and so is the structure of square matrices (MA(T),⊞,⊡,0,1) over (A(T),⊕,⊙,N,E).
N = [], E =[(1,inf,1)]
If the (A,+,.,0,1) is complete, so is the matrix semiring.
In a complete semiring we can compute the closure C = R* of matrix R using the Fletcher's algorithm:
def closure(R):
n = len(R); C = R
for k in range(n):
for u in range(n):
for v in range(n):
C[u][v] = sum(C[u][v], prod(prod(C[u][k],star(C[k][k])),C[k][v]))
C[k][k] = sum(E,C[k][k])
return(C)
where star(a) is the procedure implementing the a* operation. In the case of absorptive semiring a* = 1, and the procedure can be simplified to:
def closure(R):
n = len(R); C = R
for k in range(n):
for u in range(n):
for v in range(n):
C[u][v] = sum(C[u][v], prod(C[u][k],C[k][v]))
C[k][k] = sum(E,C[k][k])
return(C)
def plus(a,b): return(min(a,b))
def times(a,b): return(a+b)
E = [(1,inf,0)]
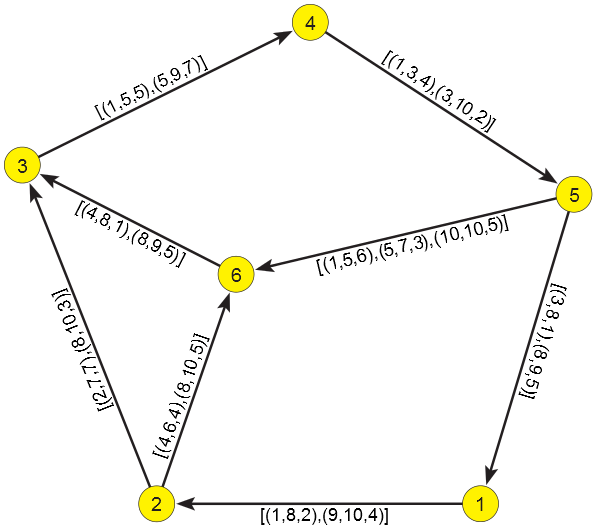
W = [[ [] for i in range(6)] for j in range(6)]
W[0][1] = [(3,8,1), (8,9,5)]
W[4][0] = [(3,8,1), (8,9,5)]
W[0][1] = [(1,8,2), (9,10,4)]
W[1][2] = [(2,7,7), (8,10,3)]
W[1][5] = [(4,6,4), (8,10,5)]
W[4][5] = [(1,5,6), (5,7,3), (10,10,5)]
W[5][2] = [(4,8,1), (8,9,5)]
W[2][3] = [(1,5,5), (5,9,7)]
W[3][4] = [(1,3,4), (3,10,2)]
def listMatrix(M):
n = len(M)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
print('(',i+1,',',j+1,') =',M[i][j])
print("matrix"); listMatrix(W)
C = closure(W)
print("closure"); listMatrix(C)
we get
matrix ( 1 , 2 ) = [(1, 8, 2), (9, 10, 4)] ( 2 , 3 ) = [(2, 7, 7), (8, 10, 3)] ( 2 , 6 ) = [(4, 6, 4), (8, 10, 5)] ( 3 , 4 ) = [(1, 5, 5), (5, 9, 7)] ( 4 , 5 ) = [(1, 3, 4), (3, 10, 2)] ( 5 , 1 ) = [(3, 8, 1), (8, 9, 5)] ( 5 , 6 ) = [(1, 5, 6), (5, 7, 3), (10, 10, 5)] ( 6 , 3 ) = [(4, 8, 1), (8, 9, 5)] closure ( 1 , 1 ) = [(1, inf, 0)] ( 1 , 2 ) = [(1, 8, 2), (9, 10, 4)] ( 1 , 3 ) = [(2, 4, 9), (4, 6, 7), (6, 7, 9), (9, 10, 7)] ( 1 , 4 ) = [(2, 4, 14), (4, 5, 12), (5, 6, 14), (6, 7, 16)] ( 1 , 5 ) = [(2, 3, 18), (3, 4, 16), (4, 5, 14), (5, 6, 16), (6, 7, 18)] ( 1 , 6 ) = [(2, 3, 24), (3, 4, 22), (4, 6, 6), (6, 7, 21), (9, 10, 9)] ( 2 , 1 ) = [(3, 4, 15), (4, 5, 13), (5, 6, 15), (6, 7, 17), (8, 9, 17)] ( 2 , 2 ) = [(1, inf, 0)] ( 2 , 3 ) = [(2, 4, 7), (4, 6, 5), (6, 7, 7), (8, 10, 3)] ( 2 , 4 ) = [(2, 4, 12), (4, 5, 10), (5, 6, 12), (6, 7, 14), (8, 9, 10)] ( 2 , 5 ) = [(2, 3, 16), (3, 4, 14), (4, 5, 12), (5, 6, 14), (6, 7, 16), (8, 9, 12)] ( 2 , 6 ) = [(2, 3, 22), (3, 4, 20), (4, 6, 4), (6, 7, 19), (8, 10, 5)] ( 3 , 1 ) = [(3, 5, 8), (5, 8, 10), (8, 9, 14)] ( 3 , 2 ) = [(3, 5, 10), (5, 8, 12)] ( 3 , 3 ) = [(1, inf, 0)] ( 3 , 4 ) = [(1, 5, 5), (5, 9, 7)] ( 3 , 5 ) = [(1, 3, 9), (3, 5, 7), (5, 9, 9)] ( 3 , 6 ) = [(1, 3, 15), (3, 5, 13), (5, 7, 12)] ( 4 , 1 ) = [(3, 8, 3), (8, 9, 7)] ( 4 , 2 ) = [(3, 8, 5)] ( 4 , 3 ) = [(3, 4, 12), (4, 5, 9), (5, 7, 6)] ( 4 , 4 ) = [(1, inf, 0)] ( 4 , 5 ) = [(1, 3, 4), (3, 10, 2)] ( 4 , 6 ) = [(1, 3, 10), (3, 5, 8), (5, 7, 5)] ( 5 , 1 ) = [(3, 8, 1), (8, 9, 5)] ( 5 , 2 ) = [(3, 8, 3)] ( 5 , 3 ) = [(3, 4, 10), (4, 5, 7), (5, 7, 4)] ( 5 , 4 ) = [(3, 4, 15), (4, 5, 12), (5, 7, 11)] ( 5 , 5 ) = [(1, inf, 0)] ( 5 , 6 ) = [(1, 5, 6), (5, 7, 3), (10, 10, 5)] ( 6 , 1 ) = [(4, 5, 9), (5, 8, 11), (8, 9, 19)] ( 6 , 2 ) = [(4, 5, 11), (5, 8, 13)] ( 6 , 3 ) = [(4, 8, 1), (8, 9, 5)] ( 6 , 4 ) = [(4, 5, 6), (5, 8, 8), (8, 9, 12)] ( 6 , 5 ) = [(4, 5, 8), (5, 8, 10), (8, 9, 14)] ( 6 , 6 ) = [(1, inf, 0)]
Temporal centrality measures
The closure matrix can be used to compute selected temporal centrality measures. For an example let us consider the measure
C(v) = ∑ {u ∈ V∖{v} : 1 / d(v,u)} / (n-1)
Assuming that for u≠v, d(v,u)≥1, the largest possible value of the sum in C(v) is n-1, attained on the central vertex of star Sn or vertices of complete graph Kn. This gives the normalization factor 1/(n-1). Therefore C(v) ∈ [0,1].
def invert(a):
c = []
for (sa,fa,va) in a:
c.append((sa,fa,1/va))
return(c)
def central(v,C):
cc = c = []; n = len(C)
for t in range(n):
if t!=v:
c = sum(c,invert(C[v][t]))
for (s,f,v) in c: cc.append((s,f,v/(n-1)))
return(cc)
ce = list(range(6))
for v in range(6): ce[v]=central(v,C)
for v in range(6): print(v+1,':',ce[v])
we get (reals were manually rounded at 4th decimal):
1 : [(1, 2, 0.1), (2, 3, 0.0083), (3, 4, 0.0091), (4, 5, 0.0143), (5, 6, 0.0125), (6, 7, 0.0095), (7, 8, 0.1),
(9, 10, 0.0222)]
2 : [(2, 3, 0.0091), (3, 4, 0.01), (4, 5, 0.0154), (5, 6, 0.0133), (6, 7, 0.0105), (8, 9, 0.0118), (9, 10, 0.04)]
3 : [(1, 3, 0.0133), (3, 5, 0.0154), (5, 8, 0.0167), (8, 9, 0.0143)]
4 : [(1, 3, 0.02), (3, 4, 0.0167), (4, 5, 0.0222), (5, 7, 0.0333), (7, 8, 0.04), (8, 9, 0.0286), (9, 10, 0.1)]
5 : [(1, 3, 0.0333), (3, 4, 0.0133), (4, 5, 0.0167), (5, 7, 0.0182), (7, 8, 0.0667), (8, 9, 0.04), (10, 10, 0.04)]
6 : [(4, 5, 0.0182), (5, 8, 0.0154), (8, 9, 0.0105)]
Examples
def binMat(A):
nr = len(A); nc = len(A[0])
B = [[ [] for i in range(nc)] for j in range(nr)]
for u in range(nr):
for v in range(nc):
B[u][v] = binary(A[u][v])
return(B)
def sumSyM(C,Rows,Cols,diag=False):
# extend for Rows and Cols are temporal partitions
n = len(C); s = []
for u in Rows:
for v in Cols:
if u>v: s = sum(s,C[v][u])
elif u<v: s = sum(s,C[u][v])
elif diag: s = sum(s,C[v][u])
return(s)
def summary(a):
vMin = tMin = inf; vMax = tMax = -inf
for (sa,fa,va) in a:
if sa < tMin: tMin = sa
if fa > tMax: tMax = fa
if va < vMin: vMin = va
elif va > vMax: vMax = va
return((tMin,tMax,vMin,vMax))
Test data
Franzosi's Italy 1919-1922
import os, re, pickle, json
from timeR import *
os.chdir('C:/Users/batagelj/work/Python/temporal/violence')
with open("violence.p","rb") as p: V = pickle.load(p)
W = V['mat']
n = len(W); All = range(n)
names = V['nam']
times = V['tim']
# listMatrix(W,names,False)
for i,name in enumerate(names): print(i,name)
# All-All
ca = sumSyM(W,All,All)
# police - 3
cb = sumSyM(W,[3],All)
# fascists - 6
cc = sumSyM(W,[6],All)
comp = {}
comp['All-All'] = ca
comp['Pol-All'] = cb
comp['Fas-All'] = cc
with open('violComp.json',mode='w',encoding='utf-8') as f:
json.dump(comp,f,indent=2)
Change to R for drawing.
> setwd("C:/Users/batagelj/work/Python/WoS/SN5/time")
> library(rjson)
> source("C:\\Users\\batagelj\\work\\Python\\WoS\\SN5\\time\\plotTime.R")
> C <- fromJSON(file="violComp.json")
> V <- fromJSON(file="violence.json")
> names(C)
[1] "Pol-All" "All-All" "Fas-All"
> names(V)
[1] "nam" "mat" "num" "tim" "tit"
> lTimes <- V$tim; lTimes <- c(lTimes,"Jan-23")
> tMin <- 1; tMax <- length(lTimes)
> times <- c(1,7,13,19,25,31,37,43,49)
> pol <- C[[1]]; wMax <- 200
> plotTime(pol,tMin,tMax,times,lTimes,wMax,h=250,main="Police",
file="violPol.pdf",PDF=TRUE)
> fas <- C[[3]]
> plotTime(fas,tMin,tMax,times,lTimes,wMax,h=250,main="Fascists",
file="violFas.pdf",PDF=TRUE,col="blue")
> all <- C[[2]]; wMax <- 700
> plotTime(all,tMin,tMax,times,lTimes,wMax,h=250,main="All-All",
file="violAll.pdf",PDF=TRUE,col="orange")
violpol.pdf - police to all
violfas.pdf - fascists to all
violall.pdf - all to all
Collaboration networks
See the pictures in Drawing the temporal quantities.
SN5
( COHEN_S , COHEN_S ) =
[(16, 17, 0.4444), (28, 29, 0.1111), (29, 30, 1.0816), (33, 34, 1.0625), (34, 35, 0.1111),
(35, 36, 1.0), (36, 37, 0.0556), (37, 38, 0.1927), (38, 39, 0.5)]
( BORGATTI_S , BORGATTI_S ) =
[(19, 20, 1.1111), (20, 21, 0.6944), (21, 22, 0.6736), (22, 23, 0.1736), (23, 24, 2.8889),
(24, 25, 0.5556), (25, 26, 0.6667), (27, 28, 0.25), (28, 29, 0.5069), (29, 30, 0.0400),
(30, 31, 0.6667), (32, 33, 0.1025), (33, 34, 0.0625), (34, 35, 0.9914), (36, 37, 1.5556),
(37, 38, 0.5), (38, 39, 0.1033)]
( BORGATTI_S , CARLEY_K ) =
[(37, 38, 0.125)]
( BORGATTI_S , FREEMAN_L ) =
[(22, 23, 0.125)]
( BORGATTI_S , WHITE_D ) =
[(22, 23, 0.0625), (25, 26, 0.2222)]
( BORGATTI_S , KRACKHAR_D ) =
[(37, 38, 0.125)]
( BORGATTI_S , JOHNSON_J ) =
[(34, 35, 0.04)]
( BORGATTI_S , EVERETT_M ) =
[(19, 20, 0.2222), (20, 21, 0.3472), (21, 22, 0.7222), (22, 23, 0.2222), (23, 26, 0.4444),
(27, 28, 0.25), (28, 29, 0.2222), (30, 31, 0.6666), (34, 35, 0.04), (36, 37, 0.2222),
(37, 38, 0.25)]
( BORGATTI_S , BOYD_J ) =
[(20, 21, 0.125), (21, 22, 0.0625)]
( CARLEY_K , CARLEY_K ) =
[(22, 23, 0.4444), (24, 25, 0.3611), (25, 26, 0.1267), (26, 27, 0.0625), (27, 28, 2.0),
(28, 29, 0.4444), (30, 31, 1.3472), (31, 32, 0.04), (33, 34, 1.0), (34, 35, 0.0625),
(35, 36, 0.3611), (37, 38, 0.4392), (38, 39, 0.5625)]
...
( HOLLAND_P , LEINHARD_S ) =
[(7, 8, 0.2222), (8, 9, 0.4444), (9, 10, 0.2222), (12, 13, 0.4444), (14, 15, 0.125)]
...
( BERNARD_H , KILLWORT_P ) =
[(7, 8, 0.2222), (9, 11, 0.2222), (11, 13, 0.125), (13, 14, 0.375), (18, 19, 0.125),
(21, 22, 0.0964), (22, 23, 0.08), (26, 27, 0.0556), (28, 29, 0.0278), (29, 30, 0.1111),
(32, 33, 0.0278), (34, 35, 0.0408), (37, 38, 0.2083)]
...
( BATAGELJ_V , BATAGELJ_V ) =
[(13, 15, 0.1111), (23, 24, 0.75), (25, 26, 1.0625), (28, 30, 1.0), (30, 31, 0.3125),
(31, 32, 0.5069), (32, 34, 0.4444), (35, 36, 0.1736), (36, 37, 0.4444), (38, 39, 0.2504)]
...
( BATAGELJ_V , FERLIGOJ_A ) =
[(13, 15, 0.2222), (23, 24, 0.5), (25, 26, 0.0625), (31, 32, 0.0625), (35, 36, 0.1736),
(38, 39, 0.0004)]
...
( DOREIAN_P , FERLIGOJ_A ) =
[(23, 24, 0.125), (25, 26, 0.125), (31, 32, 0.125), (35, 36, 0.2361), (38, 39, 0.0004)]
---------------------------
18.3.2014
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
JSON
> library(rjson)
> T <- fromJSON(file="test.json")
> names(T)
[1] "Cn" "tim" "num" "nam" "tit" "WAn"
> T$nam
[1] "A" "B" "C" "D" "E"
> T$num
[1] 5
>
> T$tit
[1] "small text example"
> T$tim
[1] "2000" "2001" "2002" "2003"
> T$Cn
[[1]]
[[1]][[1]]
[[1]][[1]][[1]]
[1] 1.00 2.00 0.25
[[1]][[1]][[2]]
[1] 2.0000 3.0000 0.2178
...
> T$Cn[[5]][[5]]
[[1]]
[1] 2.0000 3.0000 0.1089
[[2]]
[1] 3.00 4.00 0.25
>
# Batagelj, Doreian, Ferligoj
>>> BDF = [45,52,80]
>>> sumSyM(C,BDF,BDF)
[(1982, 1984, 0.4444), (1992, 1993, 1.75), (1994, 1995, 0.625), (2000, 2001, 0.625),
(2004, 2005, 1.2917), (2007, 2008, 0.0025)]
>>> sumSyM(C,BDF,BDF,True)
[(1970, 1971, 2), (1974, 1975, 1.0), (1980, 1982, 1.0), (1982, 1983, 2), (1983, 1984, 1),
(1984, 1985, 0.1111), (1985, 1986, 3.4444), (1986, 1987, 4.0), (1987, 1988, 2.0),
(1988, 1989, 5.0), (1989, 1990, 1.1111), (1990, 1991, 0.1736), (1992, 1993, 3.4444),
(1994, 1995, 4.5556), (1995, 1996, 0.1111), (1996, 1997, 1.8544), (1997, 1999, 1.0),
(1999, 2000, 0.7569), (2000, 2001, 1.4444), (2001, 2002, 2), (2002, 2003, 1.4844),
(2003, 2004, 0.1111), (2004, 2005, 2.3681), (2005, 2006, 0.5555), (2006, 2007, 2.0),
(2007, 2008, 0.2537)]
# Borgatti, Everett
>>> BE = [1, 79]
>>> sumSyM(C,BE,BE)
[(1988, 1989, 0.4444), (1989, 1990, 0.6944), (1990, 1991, 1.4444), (1991, 1992, 0.4444),
(1992, 1995, 0.8888), (1996, 1997, 0.5), (1997, 1998, 0.4444), (1999, 2000, 1.3333),
(2003, 2004, 0.08), (2005, 2006, 0.4444), (2006, 2007, 0.5)]
# Physicist: Strogatz, Watts, Newman, Holme, Park, Barabasi, Albert
>>> Fiz = [46,19,10,18,42,12,17]
>>> sumSyM(C,Fiz,Fiz)
[(1999, 2000, 1.8333), (2000, 2001, 1.2744), (2001, 2002, 0.2222), (2002, 2003, 0.9444),
(2003, 2005, 0.8889), (2005, 2006, 0.9444), (2006, 2007, 0.6667), (2007, 2008, 0.5)]
# Doreian with All
>>> n = len(C); All = range(n)
>>> sumSyM(C,[52],All)
[(1984, 1986, 0.2222), (1989, 1990, 0.2222), (1990, 1991, 0.4097), (1992, 1993, 0.375),
(1994, 1995, 0.25), (1996, 1997, 0.33), (2000, 2001, 0.25), (2001, 2002, 0.2222),
(2003, 2004, 0.2222), (2004, 2005, 0.4722), (2007, 2008, 0.0033)]
# All with All
>>> cf = sumSyM(C,All,All)
>>> cf
[(1976, 1977, 1.1389), (1977, 1978, 1.0139), (1978, 1979, 1.4583), (1979, 1980, 0.4444),
(1980, 1981, 0.25), (1981, 1982, 1.5833), (1982, 1983, 1.1944), (1983, 1984, 1.1389),
(1984, 1985, 1.3333), (1985, 1986, 0.5556), (1986, 1987, 0.8889), (1987, 1988, 0.6944),
(1988, 1989, 1.3333), (1989, 1990, 1.5139), (1990, 1991, 4.0652), (1991, 1992, 2.4694),
(1992, 1993, 4.0972), (1993, 1994, 5.0694), (1994, 1995, 2.9201), (1995, 1996, 2.7483),
(1996, 1997, 3.1183), (1997, 1998, 2.0694), (1998, 1999, 2.4705), (1999, 2000, 8.6219),
(2000, 2001, 4.4839), (2001, 2002, 3.3511), (2002, 2003, 5.0107), (2003, 2004, 3.2219),
(2004, 2005, 3.7156), (2005, 2006, 2.4583), (2006, 2007, 3.9417), (2007, 2008, 2.9678)]
>>>
Temporal indexes
TQmat (April 11, 2014); Temporal indexes
TQ class (April 16, 2014); Temporal indexes (again)